How Foreign Exchange Markets Work
Market Segments
1. Interbank or Wholesale Market
– Informal network of major banks and other financial institutions;
– Over-the-counter (OTC);
– Multiple of US$1M or equivalent in transaction size;
– 24/7 non stop aggregate activity in the whole market (worldwide).
2. Client or Retail Market
– Multinational corporations;
– Institutional investors and money managers;
– Retail investors.
Market Makers vs Currency Brokers
Market Makers (Dealers)
Market makers or dealers operate for banks or other financial institutions. Their activities are purely bilateral (no other currencies). Traditionally, it is done by phone (taped, and confirmed by mail, telex or fax). Nowadays computer ‘conversations’ dominates the way they do transactions since it is faster and safer.
They initiate a transaction by giving two-way quotes binding to an agreed limit. These two quotes are BID and ASK. Simply put, customers BUY at the ASK price and SELL at the BID price. Normally, customers will always end up paying more when buying and getting less when selling; this is due to the fact that banks need to get some commission from the trades to gain profits. The difference between BID and ASK is called spread which will be explored later on in this post.
Foreign Exchange (Currency) Brokers
Forex or currency brokers act as intermediator (middleman) for large institutions or individual investors. They do their job by shopping around finding takers of someone else’s offer.
Transaction Types
1. SPOT Transaction
Spot transaction in the interbank market is the purchase of foreign exchange, with delivery and payment to take place, normally, on the second business day after the value date (date of settlement).
In the retail market however, the settlement can be in an instant. The spot exchange rate at time t is usually notated as St.
2. FORWARD Transaction (binding contract)
A forward transaction requires deliver/ payment at a future value date of a specified amount of one currency for a specified amount of another currency. The exchange rate is established at the time of the agreement, but payment and delivery are not required until maturity (buy forward). The period can span from 30days, 90 days even 10 years.
Either party can request for a ‘broken’ (odd) date quote: a date where the delivery/ payment fall outside the standard date. This kind of transaction is usually used for import and export activities. The volume of this market is larger than the spot market. The forward exchange rate at time t for deliver/ payment at a future time T is usually notated as Ft,T.
3. Foreign Currency Swaps

A foreign currency swap agreement is a contract in which one party borrows one currency from, and simultaneously lends another to, the second party. Each party uses the repayment obligation to its counterparty as collateral and the amount of repayment is fixed at the forward rate as of the start of the contract. Put simply it is a combination of spot and forward transaction, this contract is really important for the market and the volume of this transaction dominates the market (at around 60%). This contract is usually used for Forward Hedging.
4. Foreign Currency Derivatives
Forex Options : is a derivative financial instrument that gives the right but not the obligation to exchange money denominated in one currency into another currency at a forward rate.
Forex Futures : a standardised forward contract that can be traded (exchange-traded).
Exchange Rate Quotations
Quoting Convention
1. The HC/FC Convention : the price in units of home currency (HC) per unit of foreign currency (FC) – ‘How much does ONE bread (unit of foreign currency) costs?’.
Example : ‘USD/EUR 1.33’ is an American’s natural quote for the EUR. While Eurolanders will use ‘EUR/USD 0.75’ as theirs.
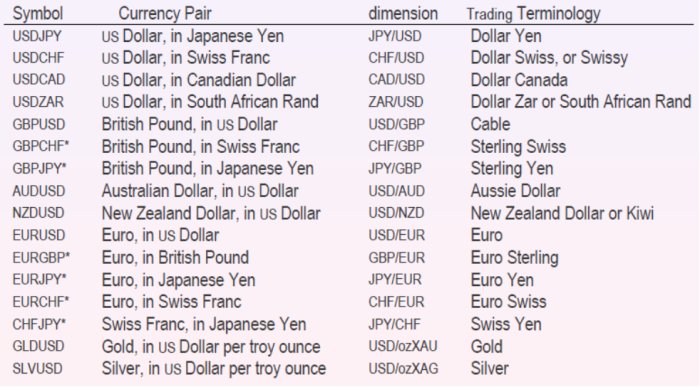
Semantics – Called ‘right‘ or ‘direct‘ quote; US: ‘US terms’. This can also be called dimension; Professionals in the financial market usually use the inverse of the dimension as the symbol. Example: ‘USDCAD or USD/CAD – 1.007’ will mean the value of USD in CAD (dimension: CAD/USD)
2. The FC/HC Convention : ‘With one Rupee you can buy 1/15th of a bread’.
This convention is usually used by several parties due to several reasons:
NY Traders against USD : Traders need a unique language; Under the Bretton Woods system, European governments had officially fixed the rates as their natural quote.
All Pros, US Traders and all Brits against GBP (similarly for ZAR, AUD and NZD) : The pound used to be intractably non-decimal (until 1967); The pound used to play the key role taken by USD after WWII, hence US traders use the unnatural quote for i.e. CHF, but natural quote for GBP.
Everybody against EUR : Euro used to be foreign, even for Eurolanders.
In practice, the standard conventions used:
Bid and Ask Quotes
When you want to buy forex, you BUY at (bank’s) ASK
When you want to sell forex, you SELL at (bank’s) BID
The difference between ask and bid’s quotes are called spread. This spread is used by banks (or any other financial institutions) to gain profit (commission). The amount of commission they can generate is equivalent to the 1/2 of the spread:
Example : EURUSD = USD/EUR = 1.1045 – 1.1047; buying is like paying midpoint (46) + cost 1 pip, and selling is like getting midpoint (46) – cost 1 pip.
Forex (including but not limited to USD, EUR and GBP) usually uses 4 decimals bracket as their measurement of change that they can experience. The smallest unit change in currency change is called 1 PIP (0.0001). In the wholesale market, traders only refer to the last two digits when asking/ offering the currency they want to exchange. This is due to the fact that the rest of the digits do not usually fluctuate as often and widely known by the market.
In retail, the amount of bid-ask spread depends on the order size (i.e. smaller for bulk)
In wholesale, the spread falls when risk of posting quote is lower (i.e. high liquidity, low volatility, normal quantity). In other words, popularity of the currency in the market, economic stability of the country’s currency as well as the size of the order determine the size of bid-ask spread.
Inverting Bid and Ask Quote
Rule: 1/ASK = BID; 1/BID = ASK – Semantically, when someone switches home currency, buying currency A becomes selling currency B.
Example : Mr. X gives JPY 1000 to the bank and receives USD 10. To Japanese, this looks like buying USD 10 at JPY/USD 100. To American this looks like selling JPY 1000 at USD/JPY 0.01.
A Reuters Conversation

Above is an example of a conversation in the chat-room which traders use to carry out transactional activities. However, with the rise of technological advancement, the forex trading nowadays are almost exclusively done by computer. With speculators (focus on profit) dominating the foreign currency market, adverse impacts to the stability to certain currency are expected. One of the most recent flash crash was on October 7th, 2016, dropping sterling’s value in the market as much as 6.1 percent.
Measuring A Change in Exchange Rates

In nominal terms,
If s > 0, the foreign currency has appreciated; if s < 0, it has depreciated.